The function of the esophagus of a frog is to transport food from the mouth to the stomach in a coordinated peristaltic wave. The esophagus is a muscular tube that contracts and relaxes rhythmically to push the food down towards the stomach, while preventing it from entering the lungs.
Frogs are fascinating amphibians that represent a diverse group of species. They have distinct structural and physiological adaptations to their environment, enabling them to thrive in a wide range of habitats. The digestive system of a frog is no exception, as it is well adapted to meet the demands of their diet, which primarily consists of insects, worms, and small aquatic creatures.
The esophagus of a frog plays a crucial role in this process, facilitating the transport of food from the mouth to the stomach. In this article, we will discuss the anatomy and function of the esophagus of a frog in detail.
Credit: matt-heymen-animalia-labs.weebly.com
What Is The Esophagus Of A Frog?
Frogs are fascinating creatures, and understanding their anatomy is crucial. The esophagus is one such component of their digestive system, which plays an essential role in their overall well-being. In this blog post, we will dive deeper into the world of the esophagus of a frog and understand its definition, location and purpose in the frog’s anatomy and digestive system.
Definition Of The Esophagus
The esophagus is a muscular tube that allows the transportation of food from the frog’s mouth to its stomach. It is a vital part of their digestive system, making it possible for them to break down their food into nutrients.
The esophagus of a frog differs from that of other animals as it doesn’t have any digestive glands.
Location Of The Esophagus In A Frog’S Anatomy
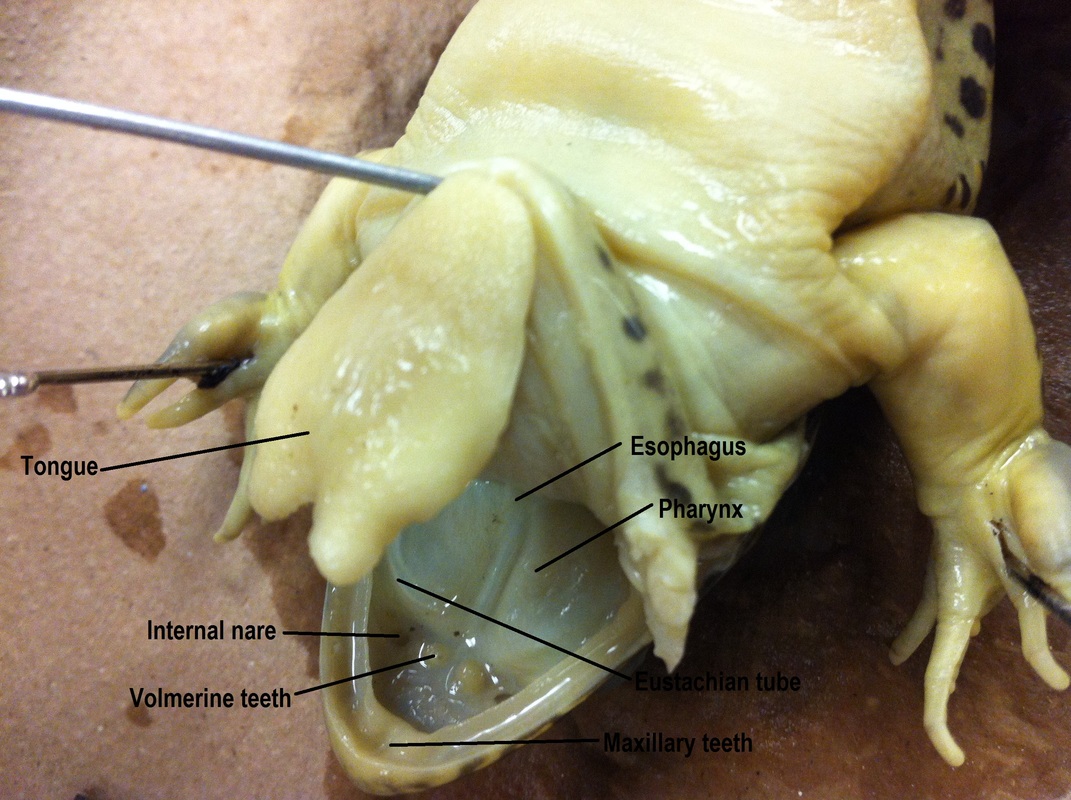
The esophagus of a frog is situated behind the glottis, which is a valve-like opening that extends to the frog’s respiratory system. It is placed just below the pharynx and runs vertically down the frog’s body before joining the stomach.
Purpose Of The Esophagus In A Frog’S Digestive System
The esophagus plays an essential role in the frog’s digestive system by transporting food from the mouth to the stomach. Once a frog has captured its prey, its eyes will move downwards, and it will use its forelimbs to push the food towards its mouth.
The esophagus will then contract and push the food towards the stomach. The esophagus acts as a storage tube for the food until it dissolves into simple nutrients and moves further to the stomach.
The esophagus of a frog is a vital component of its digestive system, responsible for transporting food from the mouth to the stomach. Understanding the function and location of the esophagus is essential to the well-being of a frog.
Functions Of The Esophagus
The esophagus is a vital part of the digestive system of a frog, connecting its mouth to its stomach. In this section, we will delve into the functions of the esophagus in a frog’s body.
Movement Of Food Through The Digestive System
The esophagus helps move food from the mouth to the stomach by contracting and relaxing the muscles in a coordinated manner. The muscles in the middle or upper part of the esophagus contract to push the food down while the muscles in the lower part of the esophagus relax to allow food to enter the stomach.
This peristaltic movement ensures that food reaches the stomach efficiently.
Secretions In The Esophagus
The esophagus produces mucus to lubricate and ease the passage of food down to the stomach. Additionally, in some frogs, such as those that feed on insects, the esophagus secretes enzymes to help break down the hard exoskeletons of the prey.
The secretion of enzymes in the esophagus is an essential adaptation in certain frog species to facilitate the digestion of their food.
The esophagus in a frog has several functions, including the movement of food from the mouth to the stomach and the secretion of mucus and enzymes. Understanding the role of the esophagus is crucial in comprehending the digestion process of a frog.
Anatomy Of The Esophagus
Frogs are unique creatures with a fascinating anatomy that enables them to thrive in their environment. One of the most crucial parts of the frog’s digestive system is the esophagus. The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, and its function is to transport food that has been swallowed to the stomach.
In this blog post, we will delve into the anatomy of the esophagus of a frog and explore its functions. Let’s get started!
Size And Shape Of The Esophagus In Frogs
The esophagus of a frog is a relatively short and narrow tube that runs down the length of the frog’s body. It measures about 2 to 3 centimeters in length and is about 3 millimeters in diameter. The esophagus starts from the back of the mouth, passes through the chest cavity, and ends at the stomach.
Layers Of The Esophagus And Their Functions
The esophagus of a frog consists of four layers, each with a distinct function. These layers are:
- Mucosa: The innermost layer of the esophagus made up of mucous membrane. Its function is to secrete mucus that lubricates the passage of food down the esophagus.
- Submucosa: The layer of connective tissue that supports the mucosa and contains blood vessels and nerves. It helps in the absorption of nutrients from the food.
- Muscularis: The middle layer of the esophagus that consists of smooth muscles arranged in circular and longitudinal bundles. It contracts and relaxes rhythmically to push the food down the esophagus and into the stomach.
- Adventitia: The outermost layer of the esophagus that consists of connective tissue and blood vessels. Its function is to anchor the esophagus to the surrounding structures.
The esophagus is a crucial part of the frog’s digestive system that plays a vital role in transporting food from the mouth to the stomach. The size and shape of the esophagus are designed to suit the frog’s requirements, and it consists of four distinct layers that work together to facilitate the smooth movement of food.
We hope you enjoyed learning about the anatomy of the esophagus of a frog!
Disorders Of The Esophagus
Function Of The Esophagus Of A Frog
Frogs are fascinating creatures that have a unique digestive system. The esophagus is a crucial part of this system and performs a vital function in the digestion of the frog’s food. The esophagus is a muscular tube that extends from the mouth to the stomach, and it plays a crucial role in pushing the food to the stomach.
Once food is swallowed, the esophagus contracts and relaxes around the food, helping to move it down to the stomach for further digestion.
Common Esophageal Disorders In Frogs
Like any other living creature, frogs can experience several disorders related to their esophagus. The following are some of the common esophageal disorders that frogs may experience:
- Esophageal impaction: Frogs may develop blockages in their esophagus due to the ingestion of large, indigestible objects. This can lead to difficulty in swallowing and regurgitation of food.
- Esophagitis: Esophagitis is the inflammation of the esophagus lining, usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. This can result in reduced appetite, regurgitation, and weight loss.
- Esophageal perforation: Perforation of the esophagus can occur due to injury or as a result of the presence of sharp objects in the esophagus. This can lead to pain, swelling, difficulty in swallowing, and infection.
How To Prevent Esophageal Disorders In Frogs
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some helpful ways to prevent esophageal disorders in frogs:
- Provide a proper diet: Offer your frog a healthy diet that is appropriate for their species. Avoid feeding them large insects or objects that may cause an obstruction.
- Provide a stress-free environment: Avoid exposing your frog to stressful environments that may contribute to the development of esophageal disorders. Keep the enclosure clean, and maintain a suitable temperature and humidity level.
- Regular monitoring: Watch your frog closely for any signs of difficulty in swallowing, regurgitation, or weight loss. Early detection can prevent the progression of esophageal disorders.
Understanding the function of the esophagus in frogs and common esophageal disorders is essential for every frog owner. With proper care and attention to their needs, esophageal disorders can be prevented, ensuring a healthy and happy life for your pet frog.
Comparing The Esophagus Of A Frog To Other Species
The esophagus of a frog is a crucial part of its digestive system. As amphibians, frogs have a unique digestive process that is different from other species. We will be comparing the esophagus of a frog to other species in terms of similarities and differences.
We will also discuss why studying the esophagus in different species is important.
Similarities And Differences Between The Esophagus Of A Frog And Other Amphibians
- Like other amphibians, the esophagus of a frog is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
- However, the length of the esophagus in frogs varies depending on the species and the size of the individual.
- For instance, some frogs have a short esophagus while others have a longer one that extends into the stomach.
- Unlike other amphibians, the esophagus of a frog lacks glands that secrete mucus. This means that food passes through the esophagus quickly, without any lubrication.
Comparison Of The Esophagus In Frogs Versus Other Species’ Digestive Systems
- Frogs are different from other species in terms of their digestive system. They have a sac-like stomach that consists of two chambers, which helps to break down food further.
- In contrast, other species, such as mammals, have a monogastric digestive system that consists of a single stomach.
- Furthermore, unlike humans and other species, frogs do not have teeth. As such, they rely on their stomach to break down food further.
Why Studying The Esophagus In Different Species Matters
- Understanding the structure and function of the esophagus in different species can help researchers gain insight into the evolution of the digestive system over time.
- It can also help them to develop new treatments and therapies for digestive disorders in humans.
- Moreover, knowing the similarities and differences between the esophagus of various species can help us understand the ecosystem and food chain better.
- By studying and comparing the esophagus in different species, we can gain a better understanding of the fundamental processes that enable survival.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is The Function Of The Esophagus Of A Frog
What Is The Function Of The Esophagus Of A Frog?
The esophagus is responsible for transporting food from the mouth to the stomach. The muscles in the esophagus contract in rhythmic waves to push food along the digestive tract.
How Long Is A Frog’S Esophagus?
The length of a frog’s esophagus varies depending on the species, but on average, it’s about 1-2 inches long. It’s shorter than a human’s esophagus due to the size of the frog.
Can A Frog Breathe Through Its Esophagus?
No, a frog cannot breathe through its esophagus. The esophagus is solely meant for the transport of food from the mouth to the stomach. Frogs breathe through their lungs and skin.
What Happens When A Frog Swallows Its Prey?
When a frog swallows its prey, the food moves from the mouth to the esophagus where it’s pushed down to the stomach by the rhythmic contractions of the esophageal muscles. The stomach then breaks down the food for digestion.
How Does The Esophagus Protect Against Choking In Frogs?
Like other animals, the esophagus uses a reflex called the “swallowing reflex. ” This protective reflex ensures that food moves down the esophagus into the stomach. The flap-like structure called the glottis also closes off the entry to the respiratory system during swallowing, preventing choking.
Conclusion
The esophagus of a frog plays a crucial role in the digestive system of these amphibians. After capturing prey with their long and sticky tongues, the esophagus helps pass the food down into the stomach. The muscular walls of the esophagus contract and push the food down, while the circular muscles prevent the food from moving back up.
This allows the frog to efficiently transport food to their stomach for digestion. Furthermore, the esophagus helps in the prevention of choking by allowing water to be pushed down into the stomach while also stopping air from getting trapped in the frog’s digestive system.
Although small in size, the function of the esophagus is vital to the well-being and survival of the frog. Understanding the role of the esophagus in the frog’s digestive system can help us understand other animal’s anatomy and the mechanisms by which they survive in the wild.
