The first amphibians appeared on Earth during the Devonian Period, about 375 million years ago. They were the descendants of fish that had begun to colonize the land. The first amphibians were probably small, primitive creatures that resembled modern-day salamanders.
Over time, they evolved into a variety of shapes and sizes, including huge predators such as the crocodile-like Mesosaurus.
When Life Conquered The Land | The Evolution of Amphibians
The first amphibians appeared on Earth during the Devonian period, about 375 million years ago. These early amphibians were fish-like creatures that could live both in water and on land. They were the first vertebrates to make the transition from water to land, and their descendants include all modern amphibians, such as frogs, salamanders, and newts.
The first amphibians were probably small and unassuming creatures, but they were an important step in the evolution of life on Earth. By moving onto land, they opened up a whole new world of possibilities for future generations of animals. Who knows what other amazing creatures we might have today if it weren’t for those pioneering Amphibians?
What was the First Amphibian?
The first amphibian was a prehistoric creature that lived during the Devonian period. This animal is thought to have resembled a modern-day salamander or newt. Amphibians were the first vertebrates to colonize land, and they played an important role in the evolution of animals.
Today, amphibians are found on every continent except Antarctica.
When Did Reptiles First Appear on Earth?
Reptiles have been on Earth for a very long time, and they were some of the first animals to appear on the planet. The earliest reptiles appeared during the Carboniferous period, which was about 300 million years ago. Reptiles were not the only animals around during this time, but they were the dominant land creatures.
There are many different types of reptiles, and they come in all shapes and sizes. Some reptiles, like snakes, are predators that hunt other animals for food. Other reptiles, like turtles, are herbivores that eat plants.
There are also reptiles that are omnivores and eat both plants and animals.
Reptiles can be found all over the world, from hot deserts to cold mountains. They have adapted to almost every type of environment on Earth.
Reptiles are even able to live in water!
The ability to adapt has helped reptiles survive for so long. They were here before dinosaurs appeared on Earth, and they’re still here today.
Who knows how long they will continue to thrive?
What Did Amphibians Evolve from?
Most people believe that amphibians evolved from fish. This is because they share many similarities with fish, such as having a tail and fins. However, there are some differences between amphibians and fish, such as the fact that amphibians have four legs instead of two.
The most popular theory is that amphibians evolved from a group of fish called rhipidistians. Rhipidistians were lobe-finned fishes that lived in the water during the Devonian period. They had both internal and external gills, which allowed them to breathe in both water and air.
Rhipidistians were able to move on land because they had strong muscles in their fins that allowed them to crawl out of the water. Over time, these muscles became stronger and developed into legs. The first amphibians probably looked like modern-day salamanders or newts.
Today, there are more than 7,000 species of amphibians living all over the world!
What Period Did Plants First Appear?
In the history of Earth, plants first appeared around 470 million years ago, during the Ordovician period. Land plants began to appear during the Silurian period, and by the Devonian period, forests had appeared on land. The first plant was probably a type of green algae.
Amphibians Characteristics
There are three main groups of amphibians: frogs and toads, salamanders, and caecilians. Amphibians are ectothermic (“cold-blooded”), tetrapod (four-legged) vertebrates that spend at least part of their life cycle in water and on land. They typically have a moist skin with no scales, although some species do have scales of various types.
Most amphibians lay their eggs in water; the larvae then hatch and spend a period of time as aquatic creatures before they transform into adults and move onto land.
Frogs and toads are perhaps the best known amphibians; they belong to the order Anura, which contains over 6,000 species. Frogs tend to be more slender than toads, with longer hind legs that enable them to make great leaps.
Toads tend to be stockier, with shorter legs; many also have poison glands on their skin that help protect them from predators. Salamanders are members of the order Caudata; they vary greatly in size and appearance but all have long tails. Caecilians are another type of amphibian; they look somewhat like worms or snakes but actually belong to the order Gymnophiona (sometimes called Apoda).
There are approximately 200 species of caecilian found throughout tropical regions around the world.
All amphibians share certain characteristics: four limbs (although some species have lost one or more pairs over the course of evolution), a moist skin without scales, underdeveloped eyesight, and a simple brain. However, there is great variation within this group of animals in terms of size, habitat preference, diet, reproduction method, etc.
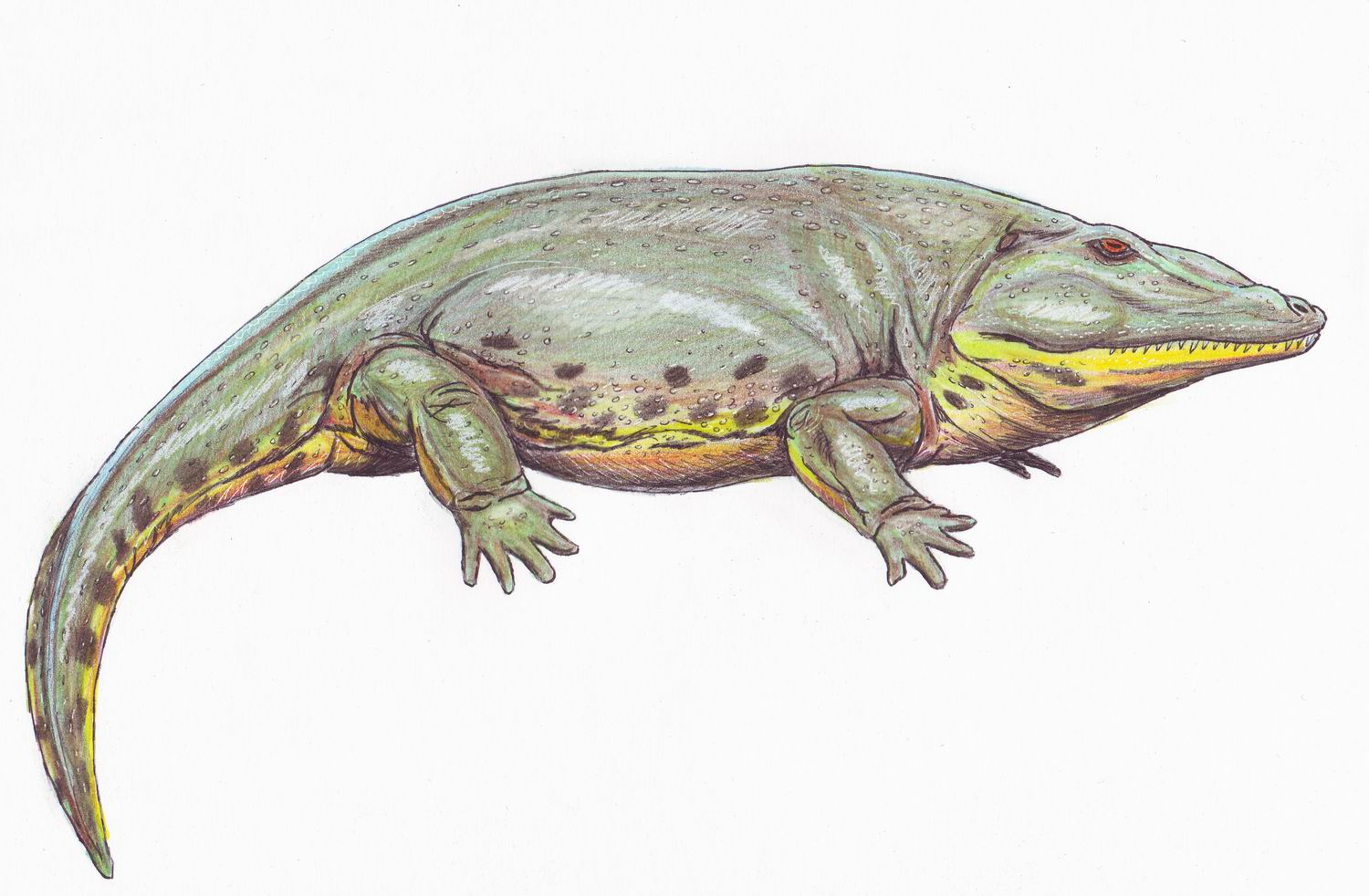
Credit: allyouneedisbiology.wordpress.com
So, When Did Amphibians First Appear on Earth?
The earliest tetrapod fossils date to the late Devonian period, around 385 million years ago. Tetrapods were generally large vertebrates with four limbs. The first amphibians probably evolved from a group of fish called lobe-finned fishes.
These fish had fleshy fins that supported their weight on land, and they could breathe air using lungs.
The first known amphibian was Ichthyostega, which lived about 375 million years ago. It had both gills and lungs, and it could live either in water or on land.
Amphibians continued to evolve throughout the Mesozoic era (252-66 million years ago), and today there are more than 7,000 species of amphibians alive.
Conclusion
Some researchers believe that amphibians first appeared on Earth during the Devonian period, which lasted from about 419 to 359 million years ago. These early amphibians were probably small, four-legged creatures that lived in wet environments and had poorly developed eyesight. Over time, amphibians evolved to better adapt to their surroundings and became more diverse in both size and appearance.
Today, there are more than 7,000 species of amphibians living on every continent except Antarctica.
